Cutting-edge tech is boosting India’s climate adaptation and mitigation efforts in myriad ways
Words by Mansi Chaturvedi and Anindya Das
As a growing economy, India continues to leverage technological innovation to enhance climate resilience and sustain its economic and industrial growth. The country is adopting innovative technologies to address the challenges posed by climate change, ensuring sustainable development while fostering economic growth.

India’s journey towards climate resilience and sustainable development is significantly bolstered by the efforts of several pioneering organisations and startups that leverage advanced technologies and innovative practices to address climate challenges and promote sustainable practices. Precision farming and smart agriculture technologies are revolutionising the Indian agriculture.
Tools like Internet of Things (IoT) sensors, drones, and satellite imagery are being used to monitor soil health, optimise water usage, and increase crop yields. These technologies help farmers adapt to changing climate conditions, ensuring food security and sustainable agricultural practices.
Future-Ready Climate Smart Innovations
To achieve a net-zero economy, India needs secure, scalable, and cost-effective alternatives. Several tech-driven projects have been implemented to enhance climate resilience, showcasing the potential of technology to drive sustainable development.
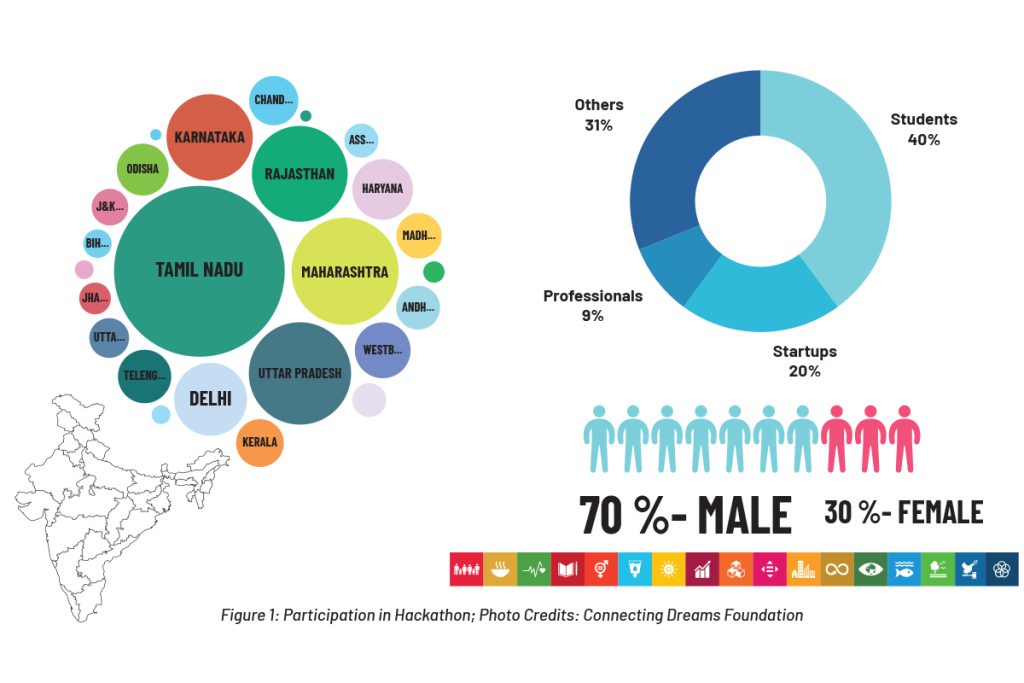
Earlier this year, the Indo-German development cooperation project ‘Climate Adaptation, Resilience and Climate Finance in Rural India (CAFRI II), commissioned by the Federal Ministry for Economic Cooperation and Development (BMZ) and implemented by the Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH, hosted the Harvesting Innovations Hackathon. The hackathon was jointly organised by GIZ India, the Bankers Institute of Rural Development (BIRD) and the Connecting Dreams Foundation (CDF), along with the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC), Government of India, and the National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD). The event aimed to harness innovative ideas and technologies for adapting to changing climate conditions in agriculture. Its focus was to address issues like unpredictable weather, rising temperatures, erratic rainfall, technology gaps, inefficient irrigation, and water resource management. Here are some notable technologies that emerged from this initiative.
AgriVijay, India’s first curated marketplace for farmers and rural households, offers a wide range of renewable and green energy products, including solar, biogas, ag-tech innovations, and organic items. Utilising an Energy Advisory Approach, AgriVijay assesses energy needs and available waste to recommend and deploy products, reducing greenhouse gas and CO2 emissions, aligned with the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).This initiative enhances energy independence and increases savings and income streams for farmers. AgriVijay spreads the benefits of renewable energy through an Artificial Intelligence (AI)-enabled chatbot, a website, dedicated call centres in local languages, field sales teams, technical support, and village-level Renewable Energy (RE) Stores. It provides high-quality, branded renewable energy products with free insurance, long-term warranties, assured after-sales service, and EMI/financing options, enabling farmers and rural households to become both producers and consumers of renewable energy. Additionally, these technologies support income diversification for rural youth and women entrepreneurs by providing livelihood and revenue opportunities through the RE stores, offering access to over two hundred products and fostering sustainable economic growth in local communities. Until now, they have benefitted up to 1,050+ farmers.

EquiCanal aims to address water scarcity and inaccessibility by boosting productivity through equitable water distribution. The districts of Koppal and Raichur in the Indian state of Karnataka benefit from irrigation facilities provided through the Tungabhadra Left Bank Canal (TLBC) system, however, the system in India faces issues of inequitable water distribution, with head-reach farmers receiving excess water while tail-end farmers suffer shortages, leading to low water use efficiency and unsustainable resource management. Mitigating the mismatch between water demand and supply during crop cycles can be achieved by developing a Decision Support System (DSS) using IoT technology, modern instrumentation for real-time data acquisition, computer modelling, and data analytics. This study in the command areas of the TLBC aims to create sustainable land and water resource management options, conserving water in distributary canals and devising a roadmap for scaling up the DSS framework across the entire TLBC. By generating periodic rosters and effectively managing canal operations, this approach benefits government departments, Water User Associations (WUAs), and farmers. It minimises conveyance losses, provides advance information on supply and demand, facilitates proper water release scheduling, enables real-time loss estimation and end-user requirement tracking, improves field water management, and enhances the overall efficiency of the distribution network.
Aigret Innovations, based in Pune, has developed AI/Machine Learning-based geo-spatial solutions for crop management and maturity prediction, including an Electrostatic Spraying System for sustainable crop yield. These solutions address the lack of precise tools for predicting harvest times and diagnosing diseases, which leads to resource waste and economic losses, particularly under extreme heat and increased vulnerability to pests and diseases. The efficient use of pesticides can result in 35-40% savings and soil preservation, while smart advisory services enable farmers to make informed decisions on prices and harvest times, thereby avoiding crop loss due to delayed harvesting. The initiative benefits from a good sample size of farmers, support from local NGOs, and financial backing.

However, organisations must be privy to the challenges of navigating regulatory hurdles, and overcoming infrastructure limitations in rural areas that pose significant barriers. To succeed, these technologies offer significant opportunities for businesses by tapping into the growing demand for sustainable agricultural solutions, accessing various funding sources, and forming partnerships with relevant stakeholders. Such technologies enable startups to create innovative, scalable business models that enhance their businesses, productivity and sustainability.
Towards a Tech-Enabled Sustainable Future
The future of climate resilience in India looks promising with continuous technological advancements and innovations. Future development cooperation initiatives can incorporate climate-smart infrastructure, using technologies like green roofs, rainwater harvesting systems, and smart grids. These climate resilient innovations support the equitable distribution of resources and can create sustainable business models that minimise waste and promote resource efficiency, presenting a significant opportunity for widespread impact.
India continues its journey as a developed nation, technological innovations play a critical role in enhancing climate resilience. With advanced technologies in renewable energy, smart agriculture, and water management, India is making significant strides towards sustainable development. Such innovations, combined with robust stakeholder engagement and inclusive practices, are key to achieving the country’s climate resilience goals. With continued investment in technology and strong partnerships, India can pave the way for a sustainable and resilient future.
Disclaimer: This article reflects the personal opinions of the authors.
The authors are Advisors – Climate Change at GIZ India


